Let’s dive into a topic that affects millions worldwide but often lurks in the shadows of public awareness: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the gastrointestinal tract, primarily characterized by two types:
An estimated 3 million adults in the United States alone are impacted, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Not only does IBD disrupts daily life but can also lead to long-term complications like an increased risk of colon cancer.
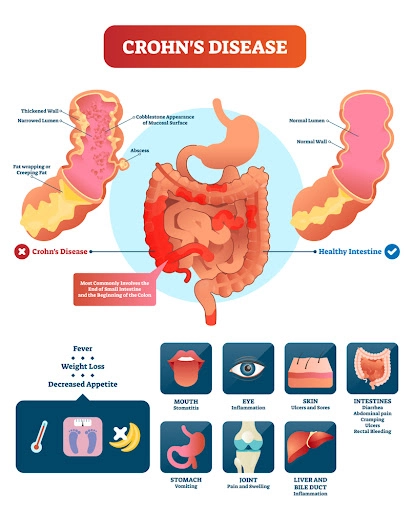
Common symptoms across both types include:
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping
- Diarrhea, which may be bloody in severe cases
- Weight Loss due to reduced Appetite and Malabsorption of Nutrients
- Fatigue, often as a result of Anemia or Severe Symptoms
Some individuals with IBD also experience additional symptoms, which may not be directly related to the gastrointestinal tract:
- Joint Pain, ranging from Mild to Severe
- Eye Inflammation, potentially leading to symptoms like Pain and Redness
- Skin Rashes, which may vary in Severity and Type
IBD can also lead to complications such as strictures in the intestines, fistulas, and an increased risk of colon cancer, especially in cases of long-standing ulcerative colitis.
This detailed exploration of IBD will guide you through its symptoms, the importance of early consultation, the surprising impacts on mental health and daily life, and intriguing insights into the use of medical marijuana (MMJ) as a treatment. With recent studies underscoring both the potential benefits and risks of cannabis in managing IBD, the conversation around this treatment option is more relevant than ever. Let’s unpack the complexities of IBD and explore how medical marijuana might offer a ray of hope for those grappling with this challenging condition.
7 Signs of IBD that require a consultation with a healthcare provider
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, especially in combination, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. They can conduct appropriate tests and evaluations to diagnose the issue and recommend a suitable treatment plan. Early intervention can help manage symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with IBD
Hidden Realities: 5 Surprising Impacts of IBD on Mental Health and Daily Life
Patients with IBD often have a higher prevalence of mental health issues, such as anxiety and depression, compared to the general population. The stress of living with a chronic illness can contribute to these conditions.
IBD is not just an adult disease. It can develop in children and teenagers, and when it does, it is often more extensive and progresses faster than in adults.
IBD can significantly impact a person’s ability to work or attend school. Frequent symptoms can lead to increased absenteeism and challenges in maintaining a regular work or school schedule.
The symptoms and severity of IBD can vary greatly among individuals. Some people may have mild symptoms, while others may experience severe and debilitating flare-ups.
IBD can affect more than just the gastrointestinal tract. It can also lead to issues in other parts of the body, such as the skin, eyes, joints, and liver.

Cannabinoid Effects in the Body
Marijuana contains compounds called cannabinoids that are similar to endocannabinoids. When cannabinoids from marijuana bind to cannabinoid receptors in the body, they can produce a variety of effects. These effects include reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and decreasing anxiety
Clinical Trials with Cannabis Extracts
In another study, patients with Crohn’s disease who were not responding well to traditional treatments were given a cannabis extract called Sativex for 8 weeks. During treatment with Sativex, patients experienced reduced inflammation and went into remission more often than those who did not receive Sativex.
Research on Cannabinoids and Gastrointestinal Inflammation
Studies have shown that cannabinoids can help to reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. In one study, rats with induced colitis were treated with a synthetic cannabinoid called WIN 55212-2. Treatment with WIN 55212-2 decreased inflammation and improved gut function in the study
The Impact of Cannabis on Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Latest 2024 Research Insights
Based on the latest research, here are some significant statistics and findings about Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and cannabis use:
A study published in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases” journal in 2023 conducted a population-based longitudinal cohort study to understand the impact of cannabis use on IBD. The study found that IBD patients who used cannabis had an increased risk for corticosteroid use, emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and opioid use. However, there was no increased risk of IBD-related surgery or death. This suggests that while cannabis might be used for symptom relief, it is associated with several poor clinical outcomes.
The study also noted differences in the impact of cannabis use between Crohn’s Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) patients. Only CD patients showed an increased risk for corticosteroid and opioid use. This indicates that the effects of cannabis can vary depending on the specific type of IBD.
Another comprehensive review of studies, as reported by NORML, highlighted that cannabis is promising in treating symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. This indicates a favorable response from patients with IBD towards cannabis therapy.
Despite some positive outcomes, the safety of cannabis and its derivatives for IBD patients remains unclear. Further research is needed to understand the long-term effects and potential risks associated with cannabis use in IBD treatment.
The findings from these studies underscore the need for more detailed and prospective research to investigate the relationships between cannabis use and IBD, particularly in understanding what drives the risks associated with cannabis use in these patients.
These findings highlight the complex nature of using cannabis in the treatment of IBD, showing both potential benefits and risks. Patients and healthcare providers need to consider these factors and stay updated with ongoing research in this area.
This source discusses how IBD patients use cannabis for symptom relief and its impact on complications. You can read more about it on Leafly’s website.
This review covers the usage of cannabinoids in IBD treatment, highlighting the benefits reported by patients, such as reduced clinical complications, symptom relief, and improved quality of life. The full text is available on PubMed.
This source provides insights into the increasing use of cannabis by IBD patients and discusses the benefits and risks associated with its use. More details can be found on PubMed.
These sources offer a comprehensive overview of the current understanding and research on the use of cannabis in the management of IBD.
5 ways cannabis has been reported to help patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):

Symptom Relief
Cannabis is commonly used by IBD patients for symptom management. Many report that it helps alleviate abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and improves overall quality of life. This is especially significant in Crohn's Disease patients, who often cite improvement in pain as a major benefit.
Assists Sleep
Many IBD patients find that cannabis helps improve their sleep quality. Good sleep is essential for overall health and can be particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic illnesses.
It’s important to note that while cannabis may help alleviate certain symptoms associated with IBD, studies have not conclusively shown that it reduces the inflammation that is at the root of the disease. Additionally, the long-term risks associated with cannabis use in IBD patients, especially in terms of exacerbating the disease or interacting with other medications, are not fully understood. Healthcare providers typically consider cannabis as a supplementary treatment rather than a primary therapy for IBD, and it is recommended to discuss its use with a treating physician.
Are you seeking relief for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)?
The good news is that in most states IBD qualifies for a medical marijuana card.
Get Your Medical Card Today!
Don't wait any longer! Take control of your health with immediate access to the treatment you need.
Apply now to access a same-day medical card and start your journey toward improving your IBD symptoms, overall health, and well-being.
Click here to apply and receive your medical card on the very same day.

IBD, is a complex disorder influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent IBD, especially due to its strong genetic component, there are several strategies that might help reduce the risk or alleviate the severity of symptoms. Here are some tips:
Diet and Nutrition
- Fiber Intake: A diet high in fiber, particularly from fruits and vegetables, may have a protective effect.
- Limiting Certain Fats: Reducing the intake of saturated fats and trans fats could be beneficial.
- Probiotics: Some studies suggest that probiotics may help maintain gut health, though their effectiveness in preventing IBD is still under investigation.
Avoiding Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Environmental Factors
Lifestyle Modifications
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for Crohn's Disease and can exacerbate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress may influence gut health. Practices such as meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can help manage stress.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall health and may help maintain a healthy digestive system.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Understanding Genetic Risks
It’s important to remember that these strategies are not foolproof and may not work for everyone. IBD is a complex condition, and whether it be medical marijuana or other treatments that might help one person may not be effective for another. If you have concerns about IBD or are experiencing symptoms, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and screening if necessary.
There is no cure for IBD, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. One such treatment is medical marijuana (MMJ). Marijuana has long been used to treat various conditions, including pain, nausea, and anxiety. In recent years, research has begun to explore the potential benefits of marijuana for treating IBD and the results are very intriguing.
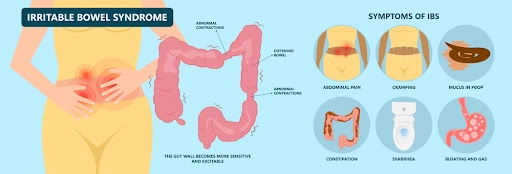
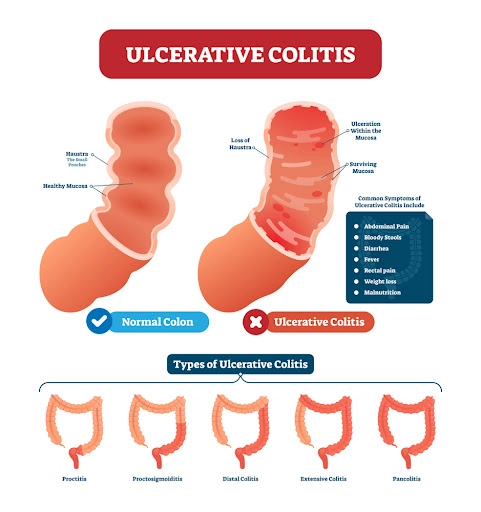
How does marijuana work with IBD
Let's take a look at the science behind it.
The human body contains a network of receptors called the endocannabinoid system. This system is involved in a variety of processes, including pain, immunity, and inflammation. Endocannabinoids are molecules that bind to these receptors and produce various effects in the body.
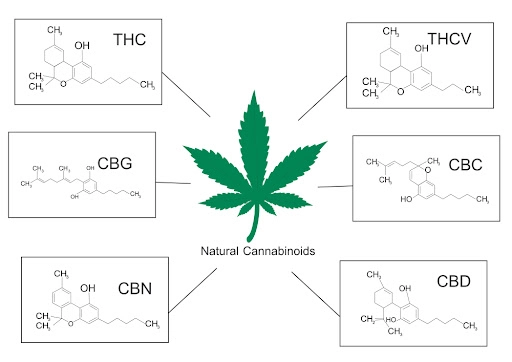
Marijuana contains compounds called cannabinoids that are similar to endocannabinoids. When cannabinoids from marijuana bind to cannabinoid receptors in the body, they can produce a variety of effects. These effects include reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and decreasing anxiety.
Studies have shown that cannabinoids can help to reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. In one study, rats with induced colitis were treated with a synthetic cannabinoid called WIN 55212-2. Treatment with WIN 55212-2 decreased inflammation and improved gut function in the study.
In another study, patients with Crohn’s disease who were not responding well to traditional treatments were given a cannabis extract called Sativex for 8 weeks. During treatment with Sativex, patients experienced reduced inflammation and went into remission more often than those who did not receive Sativex.
Cannabinoids have also been shown to possess analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. In one study, rats with induced colitis were given either a placebo or WIN 55212-2. Those rats who received WIN 55212-2 experienced less abdominal pain than those who received the placebo.
Marijuana has also been shown to be effective in treating other symptoms of IBD such as nausea and lack of appetite. In one study, patients with Crohn’s disease were given nabilone (a synthetic cannabinoid) for four weeks. Nabilone was found to be effective in treating nausea and lack of appetite while also improving quality of life measures such as sleep quality and ability to perform daily activities Furthermore, a survey of 245 adults with IBD found that nearly half of those surveyed had used cannabis in an attempt to relieve their symptoms.
Of those who had used cannabis, over 80% reported that it was effective in treating their symptoms. Benefits were reported for a variety of symptoms including pain, fatigue, diarrhea, anxiety, depression, sleep disturbance, and lack of appetite. Another survey found that 38% of Canadians with Crohn’s disease had used cannabis within the past year and seem to be having a positive experience. Overall, these studies suggest that cannabinoids may be effective in treating some symptoms associated with IBD.
Exploring the Potential of Medical Marijuana in Managing IBD Symptoms
More research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of medical marijuana for treating IBD. However, the available evidence suggests that cannabinoids may help to reduce inflammation and relieve some symptoms associated with IBD such as pain, nausea, fatigue, diarrhoea, anxiety, and lack of appetite. If you are considering using medical marijuana for your IBD symptoms, speak with your doctor to see if it may be right for you.
IBD is an approved medical condition for an Illinois medical card. If you or someone you know is experiencing painful symptoms resulting from IBD, medical marijuana may be a better option than traditional therapy or treatments. Consult a marijuana doctor to learn how cannabis can help you combat IBD symptoms.
Get Your Medical Card Today!
Are you seeking relief for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)? Don't wait any longer! Apply now to access a same-day medical card. With our streamlined process, you can quickly obtain your medical card and start your journey toward improved health and well-being.
Click here to apply and receive your medical card on the very same day.
Take control of your health with immediate access to the treatment you need. Apply today!
Legal & Medical Disclaimer
The information provided on this blog is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as, nor should it be considered a substitute for, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The content on this blog is provided “as is” and no representations are made that the content is error-free. The website takes no responsibility for errors or omissions in the content of this blog or other websites or resources that may be referenced or linked to herein. The website’s content is not intended to recommend or endorse any specific tests, physicians, procedures, opinions, or other information that may be mentioned on the site.
By using this blog, you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by this website. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not use this blog.
The information provided on this blog is for general informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as, nor should it be considered a substitute for, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The content on this blog is provided “as is” and no representations are made that the content is error-free. The website takes no responsibility for errors or omissions in the content of this blog or other websites or resources that may be referenced or linked to herein. The website’s content is not intended to recommend or endorse any specific tests, physicians, procedures, opinions, or other information that may be mentioned on the site.
By using this blog, you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by this website. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not use this blog.



